Practical Guide Correcting Color Distortion in Video Exports with AI Upscaling Tools
Practical Guide Correcting Color Distortion in Video Exports with AI Upscaling Tools - Understanding AI Upscaling for Video Color Correction
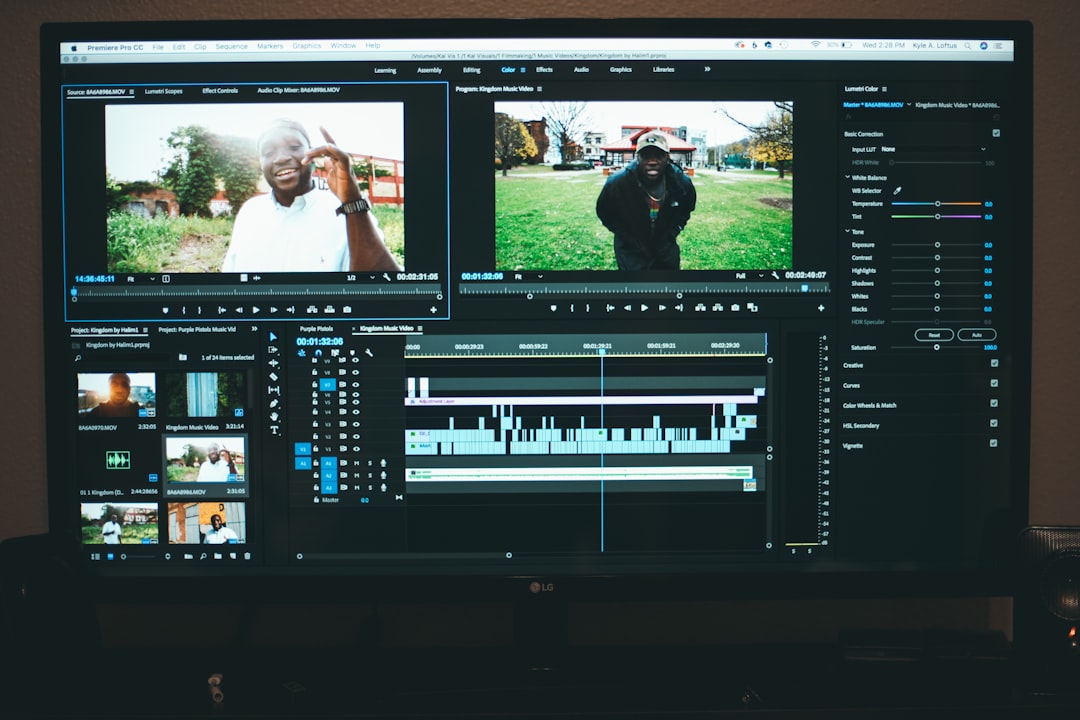
AI video upscaling is becoming increasingly important for color correction, offering a new level of control and automation for improving video quality. These tools go beyond basic adjustments like brightness and contrast, using sophisticated algorithms to enhance resolution and tackle color distortion. They can automatically refine details, remove unwanted artifacts, and generally improve the visual clarity of older or low-quality videos. The potential to upscale footage, especially from lower resolutions, is a powerful feature that can bring a significant improvement in video appearance. Choosing the right AI tool for a particular project is becoming increasingly important as the range of options available expands. It's crucial to consider the level of detail needed and the specific challenges of the video footage when selecting a tool. Ultimately, AI upscaling is becoming an indispensable part of video editing, enabling editors to achieve a level of refinement and polish previously unattainable without significant manual work. This evolution in video editing technology emphasizes how AI is revolutionizing post-production, providing streamlined workflows and improved quality.
The use of convolutional neural networks (CNNs) in AI upscaling has proven to be quite effective at preserving color fidelity, a significant advantage over older, simpler interpolation methods. These newer AI methods can analyze and address color distortions that might arise from different shooting environments, like lighting. Interestingly, some AI tools employ generative adversarial networks (GANs). These networks are trained on vast collections of high-quality videos, allowing them to generate upscaled versions that match the desired color palette and distribution found in reference material.
A key benefit of AI-driven upscaling is the ability to maintain consistent color across multiple frames. This temporal awareness allows for smoother and more natural-looking color transitions during correction. Notably, certain AI techniques also excel at reducing or even eliminating color banding, which can otherwise create undesirable abrupt gradients in the output video.
Researchers are actively developing upscaling methods with a layered approach to color correction. This lets them finely adjust brightness, saturation, and hue separately, leading to a more well-balanced and nuanced color representation in the final video. It's common practice to train AI models for color correction using datasets that expose them to a wide range of lighting conditions. This helps them become more adaptable and reliable in various recording scenarios.
However, it's important to note that the efficacy of AI upscaling depends heavily on the input video's initial quality. Low-resolution videos might not experience the same level of improvement, regardless of how advanced the AI technology used. Despite these limitations, AI upscaling techniques are proving to be quite adept at handling HDR formats. They can intelligently manage color and tone mapping to accurately convey the brighter, high-contrast details captured in these recordings.
One notable advancement in this field is the rapid increase in processing speeds of AI upscaling tools. Many can now work in real-time, which is invaluable for video professionals who frequently operate within strict deadlines. This ability to swiftly process large video files and deliver accurate color correction results is certainly driving increased interest in this emerging technology.
Practical Guide Correcting Color Distortion in Video Exports with AI Upscaling Tools - Selecting the Right AI Tool for Your Video Export Needs
The selection of an AI tool for your video exports plays a crucial role in achieving optimal color correction and enhancing the overall video quality. There's a range of options available, each with its own strengths, from tools like Topaz Video AI focused on enhancing video quality to more comprehensive editing suites like Adobe Firefly. When selecting a tool, consider the unique characteristics of your video, such as the initial resolution and the shooting conditions. This will help you choose a tool capable of effectively mitigating any color distortions present. The field of AI video tools is consistently developing, so it's essential to carefully evaluate the specific capabilities offered by each tool before committing to one. The tool should ideally align with your project's needs and ambitions. The ability to efficiently produce high-quality videos has made specialized AI tools increasingly important for content creators. The ability to quickly achieve refined, polished video exports, previously a more time-consuming process, is a significant benefit of utilizing the right AI tool.
The selection of an AI tool for color correction can significantly impact the final result, as different algorithms vary in their ability to interpret and maintain color nuances. Some might inadvertently flatten important color subtleties that are crucial for conveying the visual narrative of a video.
A common issue observed in many existing AI upscaling tools is the limited utilization of color information present in high-quality footage. Often, less than 10% of this information is used, leading to potentially inaccurate color reproduction and potentially problematic results under less conventional lighting situations.
Interestingly, certain AI tools can utilize metadata embedded within video files to refine color correction. This metadata can contain details like camera settings, location, and environmental conditions – aspects that traditional editing often overlooks. This approach allows for more contextualized color adjustments.
Advanced AI algorithms generally necessitate extensive training using diverse datasets to effectively tackle color distortion. This means that tools with limited training might struggle with videos recorded under unique lighting scenarios or utilizing uncommon color palettes.
Tools that allow for real-time user feedback can adapt their processing in response to those preferences. This dynamic adaptation leads to a more personalized color correction approach, departing from purely algorithm-driven corrections.
The resolution of the reference material used to train an AI model directly influences the upscaling outcomes. AI tools trained using high-resolution reference footage often demonstrate a better ability to accurately recreate intricate color gradients compared to those trained on lower quality sources.
Some AI upscaling tools now utilize multi-scale processing techniques. This allows engineers to refine multiple levels of detail within the video simultaneously, enhancing both color fidelity and overall image sharpness.
It's crucial to remember that some AI tools, depending on their configuration, might introduce undesirable artifacts during the upscaling process. This can potentially hinder color correction efforts if not addressed or managed during the editing phase.
The specific parameters configured within an AI model are critically important. Inappropriate parameter adjustments can result in oversaturated or excessively washed-out colors. It's not just the selection of the AI tool that matters, but also the knowledge and skills required to effectively configure it.
An intriguing trend among efficient AI tools is the increasing use of machine learning methods that identify repeating patterns in video sequences. This ability to recognize and correct color distortions across multiple clips rather than on a frame-by-frame basis significantly streamlines the editing workflow.
Practical Guide Correcting Color Distortion in Video Exports with AI Upscaling Tools - Step-by-Step Guide to Correcting Color Distortion

Step-by-Step Guide to Correcting Color Distortion
Achieving accurate and consistent color in videos is a crucial part of the editing process. This step-by-step guide provides a practical framework for fixing color problems, no matter your experience level. It emphasizes the need to carefully manage white balance, exposure, and contrast. You'll gain insights into how various video editing tools can be used to restore a more natural and appealing look to video footage.
One challenge faced is dealing with the color distortions often caused by less-than-ideal lighting scenarios, and it's important to be able to adapt techniques to these situations. It is also critical to understand the role AI upscaling tools now play in addressing color issues, improving overall video quality as part of the process.
By building a consistent workflow that incorporates these color correction steps, and carefully selecting which tools are most appropriate, video creators can greatly enhance the aesthetic appeal of their projects, resulting in a more professional and polished final product. It's an essential skill for anyone looking to move beyond simple edits to achieve a high-quality video export.
Color correction within AI upscaling often involves sophisticated techniques like mapping between different color spaces. This can help to improve the accuracy of color representation, aligning it with industry standards like Rec. 709 or DCI-P3. The ability to process multiple frames at once to maintain temporal coherence is another interesting development. It addresses flickering or color inconsistencies, which is often a problem in, for example, animated sequences where traditional methods can struggle.
It's intriguing that some AI tools can analyze a video's dynamic range to adapt their color correction approach. This allows them to manage highlights and shadows more effectively, preventing any loss of essential visual information during color adjustments. Additionally, the use of machine learning and constant refinement based on user feedback and varied types of content is enhancing the adaptability of these tools. This means they can learn and improve their color correction abilities across various scenarios.
An intriguing aspect is the AI's growing capability to identify and handle artifacts like chromatic aberrations or noise, which can negatively impact color accuracy. This artifact management is an important part of achieving high-quality results. Some AI tools even utilize multiple color models, such as RGB, CMYK, and HSL, to provide a more versatile and nuanced approach to color adjustment. It's becoming increasingly common to have real-time color grading previews integrated into these tools. This is quite useful, as it enables the user to visualize the outcome of their adjustments before committing to them, promoting a more intentional approach to color correction.
There's a focus on preserving smooth transitions between colors, known as gradients. This can enhance the overall realism in a scene, which is a subtlety often overlooked in standard video editing workflows. The integration of AI upscaling tools into familiar editing environments like Premiere Pro or DaVinci Resolve is a notable advantage. It creates a smooth workflow where color correction is seamlessly integrated with other video editing functions, which can be a significant time-saver.
Interestingly, this technology has proven particularly useful when working with historical video footage, where color distortions can be caused by outdated techniques or degradation. By implementing modern algorithms, these tools can effectively restore vintage recordings to a more accurate representation of the original colors. While it's still a developing field, AI upscaling in video is showing real promise for improving and standardizing the color correction process within video editing, especially as it becomes more seamlessly incorporated into standard workflows.
Practical Guide Correcting Color Distortion in Video Exports with AI Upscaling Tools - Common Pitfalls in AI Video Color Correction

AI-powered video color correction offers exciting possibilities, but it's important to be aware of potential pitfalls that can impact the quality of the final result. Over-reliance on automated adjustments without careful fine-tuning can lead to a lack of depth in the colors, producing a dull or overly processed look. Furthermore, neglecting the context of the original video footage, including factors like the intended mood and the lighting conditions under which it was recorded, can easily lead to color adjustments that don't enhance the video's intended message. The choice of AI tool matters a great deal; certain tools might not effectively handle the full range of color information in the footage, especially under complex lighting situations, leading to less-than-ideal outcomes.
Failing to monitor the color correction process diligently and neglecting real-time feedback mechanisms can also cause problems. It's easy to miss color distortions or artifacts in the video that may not be immediately obvious. These oversights can severely detract from the desired aesthetic and professionalism of your video export. Understanding these potential difficulties and actively addressing them during the color correction process is key to achieving professional-looking video exports.
### Surprising Facts About Common Pitfalls in AI Video Color Correction
The use of AI for color correction in videos is undeniably promising, yet it's not without its hurdles. While these tools often excel at enhancing video quality and streamlining workflows, there are some surprising limitations that can lead to unexpected issues. For example, the accuracy of AI-based color correction is highly dependent on the data used to train the models. If the training datasets are not diverse enough, they might fail to handle videos from unique filming environments, producing less accurate color results.
This reliance on training data isn't the only pitfall. Many algorithms used in these tools can inadvertently simplify complex color variations, flattening out the details that give a video its depth and visual impact. One common issue is the application of excessive smoothing filters which, while meant to improve appearance, can erode crucial color transitions.
Interestingly, some of these tools, even as they attempt to clean up the visual output, can actually introduce new color issues during processing. This can result in unnatural color borders, strange color shifts, or other anomalies that diminish the visual integrity of the final video. Additionally, videos containing quick movements can experience color flickering or inconsistency issues because the tools don't always accurately handle temporal coherence across frames.
The tools haven't fully grasped the value of metadata within video files, frequently failing to utilize it in the color correction process. Camera settings, lighting conditions, and recording location details contained within metadata can often improve the overall result, but are regularly ignored.
Another hurdle is that many AI tools have an overwhelming number of settings. While this offers immense customizability, it can easily overwhelm users, leading to incorrect adjustments and unexpected outcomes. These incorrect settings can cause unwanted color shifts or excessively flat or exaggerated color gradients.
Furthermore, users might rely too heavily on default settings, potentially missing opportunities to fine-tune the correction for unique footage characteristics. This reliance on defaults often results in generic outcomes rather than the unique visual style that creators aim for.
The quality of the training data also plays a big part in the success of the AI tool. Tools trained on high-quality footage tend to perform significantly better than those trained on lower-quality data. This difference highlights the vital role of video quality in determining the accuracy of color rendition during the upscaling process.
Surprisingly, some tools have limitations on the type of formats they can output in, impacting the viewing experience across different platforms. Each platform has unique color management demands, and if the video can't be easily converted into those formats, it can impact viewers.
One of the most puzzling limitations is the lack of user interaction and adaptation in many tools. Often, they follow rigidly predefined algorithms and don't accommodate user feedback or evolving aesthetics, which can curb creative freedom. Creators often find their intended styles not being properly reflected in the final color-corrected output. These various shortcomings demonstrate that, despite the promise of AI, the evolution of color correction in AI-enhanced video editing still has a ways to go.
Practical Guide Correcting Color Distortion in Video Exports with AI Upscaling Tools - Optimizing Output Settings for Best Results

When using AI upscaling tools for color correction, getting the best results hinges on fine-tuning the output settings. Choosing the right output resolution, compression, and color space can make a big difference in the final video's quality, making sure the enhanced colors look natural. A lot of current AI tools let you export in various formats, including super high resolutions like 16K, but it's crucial to know how to customize these settings for your project. If the output settings aren't right, it can create unwanted visual flaws or make the colors inaccurate. This makes it vital to carefully adjust these settings during the exporting phase. AI upscaling technology is constantly improving, so it's helpful to stay up-to-date on new features and methods for optimizing output for those who want to create the best quality videos.
When it comes to getting the best results from AI video upscaling, particularly concerning color correction, the output settings play a surprisingly important role. For instance, the bitrate you choose for the exported video directly impacts the level of color detail that's preserved. Higher bitrates, while resulting in larger file sizes, generally translate into better color fidelity, especially within smooth color transitions, helping reduce the appearance of banding and overall boosting the quality of the output.
Similarly, the color space you pick for export can have a profound effect on how the video handles color. Different color spaces, like Rec. 709 and DCI-P3, offer distinct ranges of colors that can be represented, and understanding the capabilities of each space is important to ensuring your output looks the way you intend, especially if you're aiming for a particular level of vibrancy or accuracy.
Interestingly, many AI tools can utilize a video's dynamic range during the export process, effectively fine-tuning brightness and color within high-contrast scenes. This can be extremely beneficial for retaining detail in both dark shadows and bright highlights, significantly improving the perceived quality of the final product when optimized correctly.
However, it's crucial to ensure that your chosen settings maintain temporal coherence. If settings aren't chosen well, you can end up with frames that aren't color-consistent, leading to distracting and unnatural color fluctuations that can break immersion for the viewer. It's important to consider these inconsistencies when you're optimizing for smoother and more realistic output.
The export format you choose also influences color accuracy. Not all formats are created equal when it comes to preserving color information. Certain formats might not offer support for advanced color profiles, potentially limiting the accuracy of the colors in the final exported video. Choosing the correct format, understanding its capabilities, is important for maintaining quality across different platforms.
It's interesting that even the efficiency of your GPU can be factored into achieving better color in the final export. Optimizing certain settings can allow your graphics card to efficiently handle the video processing during export, speeding up the overall process while maintaining a high level of color quality.
Making use of real-time preview features within your video editing software is quite useful for understanding the effect of output settings on color before you finalize the export. It allows for more informed decisions about what adjustments to make for the best possible output. It's quite revealing to see the impact of different settings in real-time, and it fosters more deliberate decisions on color correction.
Creating custom color profiles for different output destinations is another strategy that ensures your video looks its best across various platforms. For instance, optimizing the colors specifically for HDR screens versus standard screens helps maintain accurate color rendition on the intended display type.
Certain export protocols are designed to prioritize color accuracy during compression. These options, while sometimes increasing file size, are worth considering for creators who want to maintain the integrity of their color choices.
It's fascinating to see how artificial intelligence, for all its advancements, sometimes falls short. Sometimes, the algorithms that are applied during video processing can, inadvertently, overly soften color gradients. So even with AI, you need to carefully assess the strengths and limitations of the tool and the desired output to achieve the most accurate and aesthetically pleasing results in your color correction process.
Practical Guide Correcting Color Distortion in Video Exports with AI Upscaling Tools - Balancing AI Enhancement with Original Video Quality
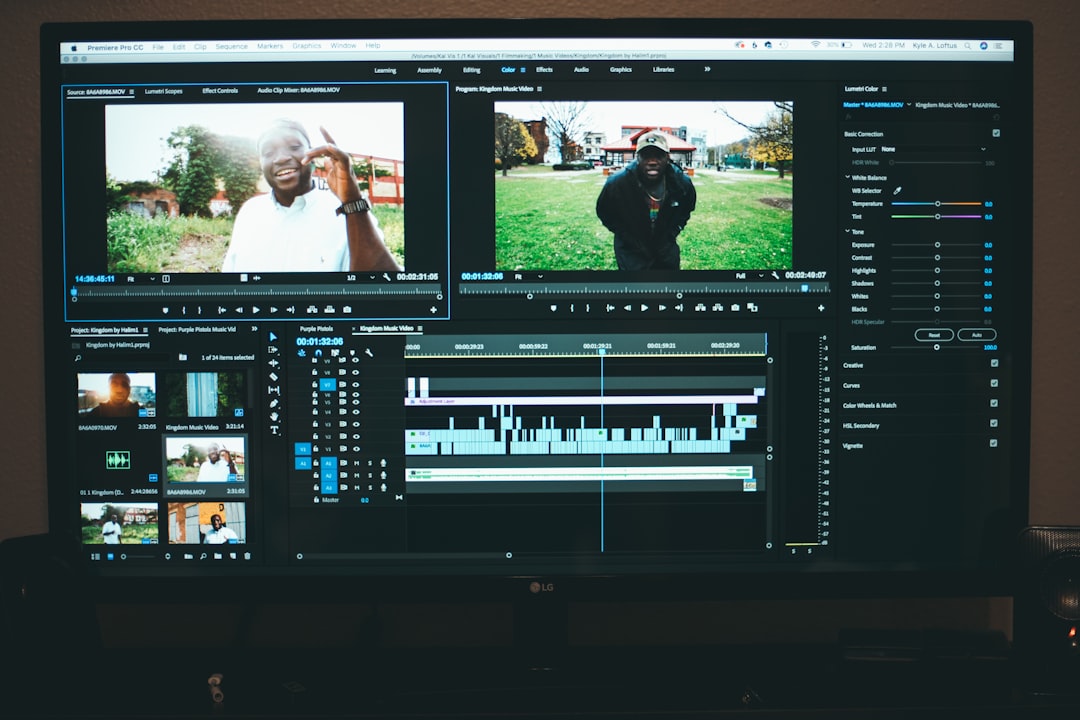
When using AI for video enhancement, especially for color correction, it's crucial to balance the benefits of the AI with maintaining the original video's quality. These AI tools are incredibly useful for fixing color distortions and upscaling resolutions, but they can sometimes change the video too much, making it look unnatural or losing the original artistic intent. The difficulty is using the AI tools without sacrificing the intricate details and subtle colors that make the original video unique. Over-relying on automatic adjustments can result in a processed look that takes away from the intended aesthetic of the video. As AI video tools are becoming more advanced, editors need a more balanced approach to how they are integrated into video editing. This ensures the desired improvements to quality are made without sacrificing the original video's visual integrity.
When it comes to enhancing video quality with AI, maintaining the original video's color integrity is paramount. Modern AI upscaling tools, powered by convolutional neural networks (CNNs), show promise in this area. These networks excel at identifying and rectifying subtle color distortions that often arise from various lighting conditions. It's fascinating how they can discern and address these nuances that traditional methods often miss.
Some tools even employ generative adversarial networks (GANs). These networks are trained using massive libraries of high-quality videos, teaching them to generate upscaled content that closely mimics the original video's colors and style. This type of approach makes for very interesting possibilities for more artistic or visually stylized projects.
Maintaining consistent colors across multiple frames, which is known as temporal consistency, is another benefit of these AI methods. This is especially noticeable in videos with dynamic action or animations, as it promotes a more natural and fluid experience for the viewer. It's quite impressive how effectively they can manage this aspect of video enhancement.
Researchers are exploring layered approaches to color correction. Rather than a one-size-fits-all correction, these methods allow for distinct modifications to elements such as brightness, saturation, and hue. It's like having a more sophisticated palette of control, potentially offering more nuance in the final results.
However, there's a catch: the effectiveness of AI upscaling often relies on the quality and variety of data used to train the algorithms. If a tool hasn't been trained with a broad range of lighting situations or artistic styles, it might struggle to handle videos with unique color palettes or lighting, leading to some questionable results.
Thankfully, some of these tools incorporate real-time feedback features. This gives the user a level of control over the color correction process, helping to refine the output to match their artistic vision. This dynamic approach reduces reliance on rigid, algorithm-driven adjustments, allowing for more personalized outcomes.
Another interesting factor is the impact of high-resolution training data. AI models trained with high-quality reference material usually excel at accurately recreating color gradients and other fine details compared to those trained with lower-resolution or poorer quality material. It's a reminder of the importance of ensuring the datasets used in training are as comprehensive as possible.
It's not all rosy though. One issue that's often observed is that automatic adjustments sometimes oversimplify complex color variations. This can result in videos that appear somewhat dull or devoid of the depth they originally had. This loss of depth in favor of over-smoothing, in pursuit of a technically better-looking video, needs to be considered when these tools are used.
Additionally, AI tools often overlook valuable metadata within video files. This metadata contains essential data like camera settings and environmental conditions – which might be helpful for a more informed color correction approach. Neglecting this data could mean missed opportunities for more nuanced and accurate corrections.
Ultimately, the final output's quality depends greatly on the chosen export format. Each format supports a particular range of color profiles, and choosing the right one for the target platform can be critical to maintaining the video's intended color fidelity. For example, if a specific color palette is crucial to a project, understanding how the export format handles that palette is an important consideration.
In conclusion, while the promise of AI-driven color correction is substantial, there are areas that require further refinement. It's crucial for creators to be aware of the capabilities and limitations of the tools they're using and to exercise informed decision-making to achieve the best possible outcome for their projects. This field is consistently evolving, and as tools mature, they will hopefully better handle edge cases and offer greater creative control.
More Posts from ai-videoupscale.com: